Lake Faticalawi isn’t your average body of water. Tucked away like a hidden gem it offers a unique blend of natural beauty and intriguing mysteries that keep visitors coming back for more. Whether you’re a nature lover or just someone who enjoys a good story, this lake has something special that sets it apart from the rest.
From its crystal-clear waters to the rare wildlife that calls it home, Lake Faticalawi invites exploration and wonder. It’s not just a place to see but an experience to savor—a perfect escape from the ordinary. Dive in and discover why this lake is making waves in both travel circles and local legends.
Overview of Lake Faticalawi
Lake Faticalawi captures attention with its pristine waters and unique environment. It stands out as a natural gem offering more than visual beauty.
Location and Geography
Lake Faticalawi lies within a remote, mountainous region, making it an isolated spot that preserves its untouched nature. It covers approximately 15 square miles, with a depth reaching 120 feet in some areas. Surrounded by dense forests and rocky terrain, it benefits from a microclimate that maintains cooler temperatures year-round. Clear waters reflect the sky, revealing rare underwater formations unique to this lake. Its location near the border of two ecological zones, forest and alpine, fosters a diverse ecosystem not commonly found in nearby lakes.
Historical Significance
Lake Faticalawi holds a rich history tied to indigenous communities who revered it as a sacred site. Archaeological evidence shows settlements dating back over 1,000 years along its shores. Early explorers documented the lake in 18th-century journals, noting its importance for trade and spiritual rituals. Legends passed through generations emphasize the lake’s mysterious qualities and its role in local folklore. This historical depth adds cultural value that draws historians and tourists eager to uncover its stories.
Unique Ecological Features
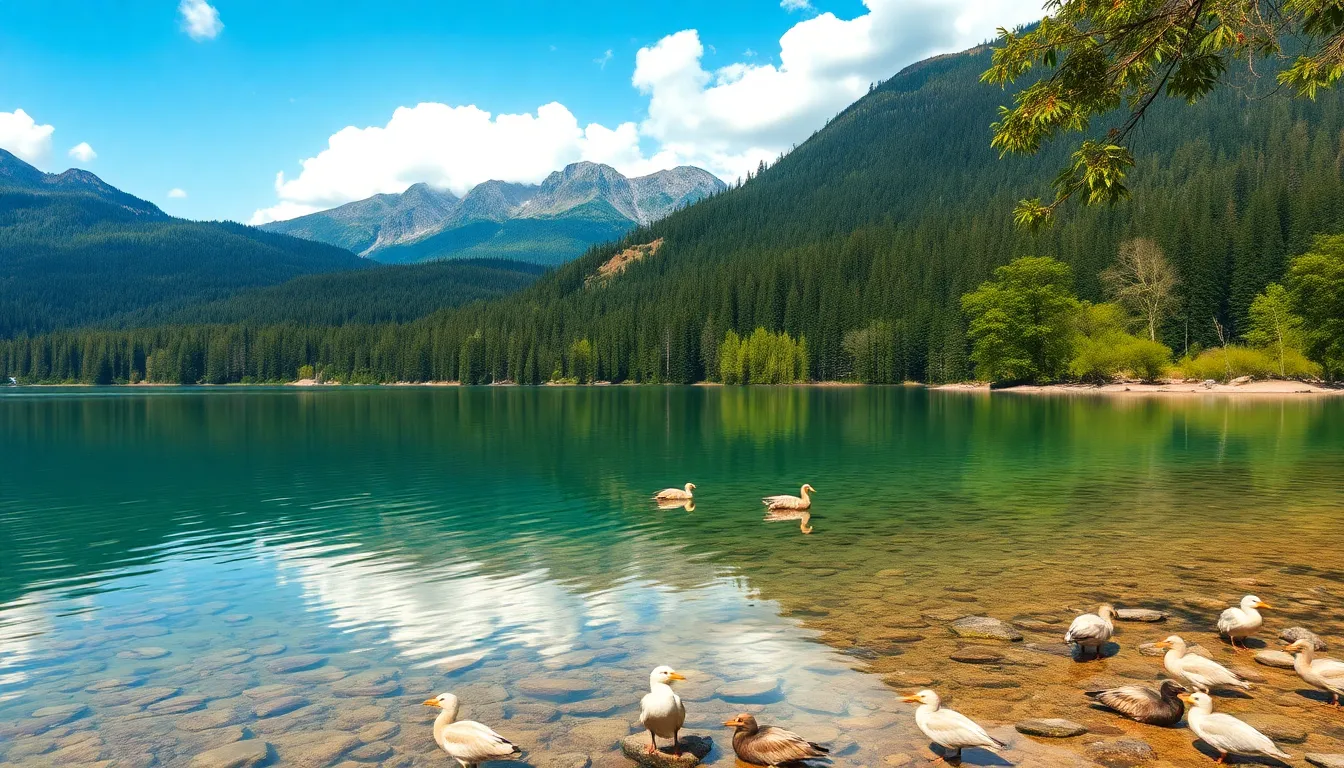

Lake Faticalawi boasts a range of ecological traits that set it apart in its remote mountainous setting. Its pristine environment supports intricate natural processes that sustain diverse life and water purity.
Biodiversity and Wildlife
The lake’s surroundings host a mix of forest and alpine species rarely found together. Fish species, such as native trout and whitefish, thrive in its clear waters. Migratory birds, including some endangered types like the alpine chough and golden eagle, use the lake as a stopover. Amphibians and reptiles native to both ecosystems inhabit the shoreline. Mammals such as marmots and pine martens contribute to this complex food web. Flora near the lake includes rare alpine wildflowers and coniferous trees. This biodiversity reflects the unique ecological niche created by the lake’s microclimate and isolation.
Water Quality and Hydrology
Lake Faticalawi maintains exceptional water clarity due to low nutrient input and limited pollution sources. It reaches depths of 120 feet, allowing thermal stratification that supports oxygen-rich lower layers. Seasonal melting glaciers and mountain springs feed the lake, sustaining stable water levels year-round. Its hydrology supports rare underwater formations visible through the transparent surface. The combination of cold temperatures and water purity inhibits algae overgrowth, preserving aquatic health. These hydrological features enable the lake’s unique ecosystems to flourish with minimal human impact.
Cultural and Social Importance
Lake Faticalawi holds deep cultural and social significance for surrounding communities. It serves as a focal point for traditions and gathers locals around shared heritage and respect for nature.
Local Communities and Traditions
Indigenous groups near Lake Faticalawi celebrate annual ceremonies honoring the lake’s spiritual role. These events include music, dance, and rituals passed down for centuries. Local folklore often features the lake as a guardian entity, reinforcing community bonds and reverence for the environment. Artisans create crafts inspired by the lake’s unique flora and fauna, supporting cultural expression and economy. Elders teach youth about sustainable resource use, ensuring traditions endure alongside environmental stewardship.
Recreational Activities and Tourism
Tourism around Lake Faticalawi focuses on eco-friendly practices that protect its pristine state. Visitors enjoy hiking trails offering views of the lake’s clear waters and diverse wildlife. Fishing, especially for native trout, attracts sport anglers seeking a challenge in the lake’s cool depths. Kayaking and paddleboarding are popular on calm days, allowing close interaction with the aquatic environment. Guided tours provide insights into the lake’s ecology and cultural history, enriching visitor experience while promoting conservation.
Conservation Efforts and Challenges
Lake Faticalawi benefits from active conservation efforts aimed at preserving its unique ecosystem and cultural heritage. Protecting this natural gem requires addressing environmental threats while supporting sustainable local practices.
Environmental Protection Initiatives
Several organizations collaborate to maintain Lake Faticalawi’s pristine condition. Local authorities enforce strict regulations limiting pollution and restricting development in surrounding areas. Community-led programs promote reforestation and habitat restoration, which encourage biodiversity around the lake. Scientific monitoring tracks water quality and wildlife populations, ensuring early detection of ecological changes. Additionally, indigenous groups partner in stewardship, integrating traditional knowledge into modern conservation strategies. Eco-tourism guidelines prioritize minimal environmental impact to balance visitor access with long-term preservation. These combined initiatives sustain Lake Faticalawi’s rare natural environment and uphold its ecological integrity.
Threats Facing Lake Faticalawi
Human activity presents significant risks to Lake Faticalawi’s fragile ecosystem. Unsustainable tourism, including overfishing and unregulated boating, can disrupt aquatic life and increase erosion. Agricultural runoff nearby poses threats through nutrient loading, which may reduce water clarity and harm sensitive species. Climate change impacts, such as altered precipitation patterns and glacial melt, affect hydrological balance and habitat stability. Illegal logging and land conversion further endanger surrounding forests crucial for biodiversity. Despite protective measures, enforcement challenges limit effectiveness in some areas. Continuous vigilance and adaptive management remain essential to address these ongoing environmental pressures.
Conclusion
Lake Faticalawi stands out as a rare blend of natural beauty, rich history, and vibrant culture. Its untouched environment and unique ecosystem create a sanctuary for wildlife and a peaceful retreat for visitors seeking more than just a destination.
The lake’s ongoing conservation efforts highlight the importance of protecting such irreplaceable places. As interest grows, balancing tourism with preservation will be key to maintaining its special charm for generations to come.












Discussion about this post