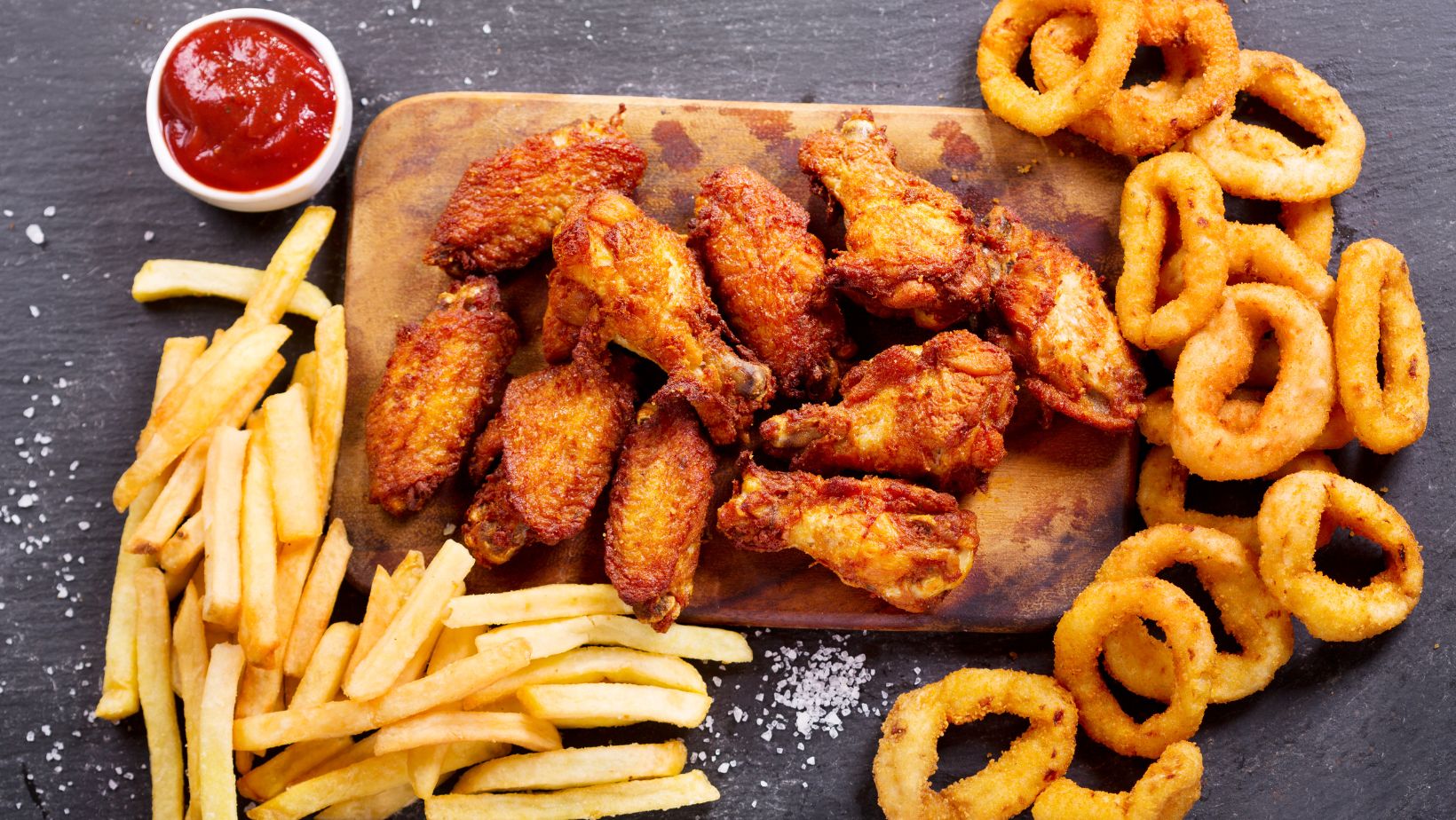
Many people don’t realize how much their daily diet affects their prostate health. Certain foods can make symptoms worse and increase the risk of prostate problems. Foods like red and processed meats, fried snacks, full-fat dairy, and sugary drinks have been shown to negatively impact the prostate.
People looking to support their prostate should know that changing what they eat can make a difference. Along with trying healthy eating habits, some turn to natural prostate health supplements as an extra way to care for their bodies. This combined approach can be helpful for those wanting to take control of their prostate health.
Key Takeaways
- Some foods can increase risk of prostate issues.
- Healthy eating and lifestyle changes support better prostate health.
- Natural prostate health supplements are often used for extra support.
Worst Foods for Prostate Health: What to Avoid and Why
Certain foods play a major role in aggravating prostate problems, including prostate cancer risk, prostatitis, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and urinary symptoms. These foods tend to increase inflammation, disrupt hormones, and support harmful cellular changes in the prostate.
Red and Processed Meats
Red and processed meats, such as beef, sausage, bacon, and hot dogs, have been linked to a greater risk of prostate cancer and other prostate problems. Eating high amounts of these meats can create harmful byproducts during cooking, such as heterocyclic amines and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
These compounds are linked to cancer risk through ongoing inflammation and oxidative stress in prostate tissue. High intake of saturated fats found in these meats also contributes to chronic inflammation, making conditions like chronic prostatitis and BPH more likely.
Processed meats contain high sodium and preservatives that may worsen urinary symptoms and affect overall prostate health. Several studies show a pattern where diets high in red or processed meats are more likely to be inflammatory and put men at a higher risk for prostate disease.
Dairy Products and Full-Fat Dairy
Dairy products, especially full-fat types like whole milk, cream, and cheese, can impact prostate health in several ways. Regular intake of high-fat dairy is linked to a higher risk of prostate cancer and may also influence hormone levels.
Full-fat dairy increases cholesterol and raises levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), a hormone linked to cell growth and potential hormonal imbalance in the prostate. Too much calcium from dairy has also been pointed out as a possible risk for prostate cancer, especially in those consuming large quantities.
These foods may also raise inflammation markers, making them foods to avoid for anyone experiencing prostatitis or other prostate symptoms. Skipping or limiting high-fat dairy can help manage prostate health better over time.
Fried Foods and Trans Fats
Fried foods, such as french fries, fried chicken, donuts, and chips, are high in trans fats and saturated fats. Trans fats are especially concerning, as they promote inflammation in the body, which can worsen prostate problems and increase the risk of chronic inflammatory diseases, including cancer.
Frying produces byproducts that are thought to contribute to oxidative stress and may trigger or worsen chronic inflammation in the prostate. Regular consumption of these foods also tends to raise cholesterol, another factor linked to prostate enlargement and worsening urinary symptoms.
High intake of trans fats has also been connected to increased cancer risk and poor outcomes in individuals with prostate disease. Reducing fried foods can therefore directly reduce both inflammation and negative hormone changes related to the prostate.
Sugary Foods and Refined Carbohydrates
Foods and drinks high in refined sugars and simple carbohydrates, such as sodas, candy, pastries, and white bread, lead to rapid blood sugar spikes and insulin resistance. High sugar intake has been associated with problems like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), chronic prostatitis, and even prostate cancer.
Sugar-sweetened beverages and snacks often contain high-fructose corn syrup, which may promote weight gain, worsen hormonal balance, and increase inflammation in the body. This inflammation can affect the prostate and worsen symptoms over time.
High consumption of refined carbohydrates encourages a more inflammatory diet and may increase oxidative stress on the prostate. Limiting sugary foods and choosing whole grains instead may reduce urinary symptoms and lower the risk of developing prostate problems.
Additional Dietary Factors and Lifestyle Changes for Better Prostate Health
Small shifts in daily habits, including reducing certain drinks and choosing whole foods, can make a difference for prostate health. Specific changes in food and drink choices help with managing hormonal balance and minimizing inflammation.
Alcohol and Caffeine Intake
Alcohol and caffeine may affect hormonal balance, leading to more prostate problems and urinary symptoms. Drinking too much alcohol, especially beer and spirits, can irritate the bladder and raise inflammation in the body. Alcohol also affects the way hormones work, which may make symptoms of prostate enlargement worse over time.
Caffeine, found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and some sodas, may increase urinary frequency and urgency. This can add stress to the bladder and prostate, especially at night. People who already have urinary symptoms may notice more discomfort after drinking drinks with a lot of caffeine or alcohol. Staying aware of how much is consumed and limiting intake can help make symptoms less bothersome.
High-Sodium and Artificial Additives
Eating too much salt is linked to high blood pressure and can stress the kidneys and bladder. Many canned foods and processed meats are high in sodium and may contain artificial additives like nitrates and nitrites. These additives are used for flavor and to keep food fresh, but they are also linked to inflammation and may increase risks for prostate problems.
A simple way to lower sodium intake is to choose fresh or frozen foods without added salt. It also helps to check food labels for sodium and artificial ingredients. Avoiding processed foods, deli meats, and salty snacks can also lower the risk of urinary problems and hormone disruption.
Foods to Limit
- Processed meats (bacon, sausage, hot dogs)
- Canned soups
- Ready-to-eat meals
- Chips and salted snacks
Plant-Based and Nutrient-Rich Food Alternatives
Plant-based diets may support prostate health because they are high in antioxidants, fiber, and polyphenols. Foods like tomatoes, which are rich in lycopene, and cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cabbage, and cauliflower help lower inflammation and support hormonal balance. Lycopene has been studied for its possible role in reducing the risk of prostate issues.
Whole grains, soy, nuts, and seeds provide fiber and omega-3 fatty acids, which may help manage inflammation. Zinc, found in beans and nuts, plays a part in hormone function and prostate health. Eating more plant-based foods and following a Mediterranean diet with fish, healthy oils, and plenty of vegetables supports long-term prostate well-being.
Conclusion
Foods high in saturated fat, processed meats, and added sugars are not supportive of prostate health. Eating these items often may raise the chance of inflammation and other prostate problems.
Choosing more fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains is a better way to support the prostate. Limiting fast food, fried food, and salty snacks can also make a difference.
Small changes in daily eating habits can lead to healthier outcomes for the prostate. Balanced meals and mindful choices are effective ways to reduce possible risks.














Discussion about this post